The Note of Digital Circuits by Westfox
Author: Westfox, Gryffindor, Class of 2023
Link: The Note of Digital Circuits by Westfox
这份文档主要讲解了数字电路的基础知识和相关概念。内容涵盖了从数制、逻辑门到时序电路和组合逻辑电路的各个方面。以下是内容的简要概括:
-
数制与转换:
- 介绍了位值数制的概念,强调了不同位置的权值和进制之间的关系,涉及常用的数制(十进制、二进制、八进制、十六进制)。
- 讨论了如何在不同进制之间进行转换,特别是十进制与其他进制的相互转换方法。
-
逻辑代数与布尔代数:
- 讲解了布尔代数的基本运算,如加法(OR)、乘法(AND)、取反(NOT),并引入了德摩根定律和共识定理。
- 介绍了开关代数及其在数字电路中的应用,讨论了逻辑表达式、真值表的使用和化简方法,如卡诺图(K-map)用于化简布尔表达式。
-
基本电路模块:
- 加法器:解释了半加器和全加器的工作原理及其实现方式,广泛应用于计算机和数字系统中。
- 比较器:用于比较两个二进制数的大小,输出判断结果,广泛应用于排序和决策中。
- 编码器/解码器:用于编码和解码信息,帮助实现信号转换和路由。
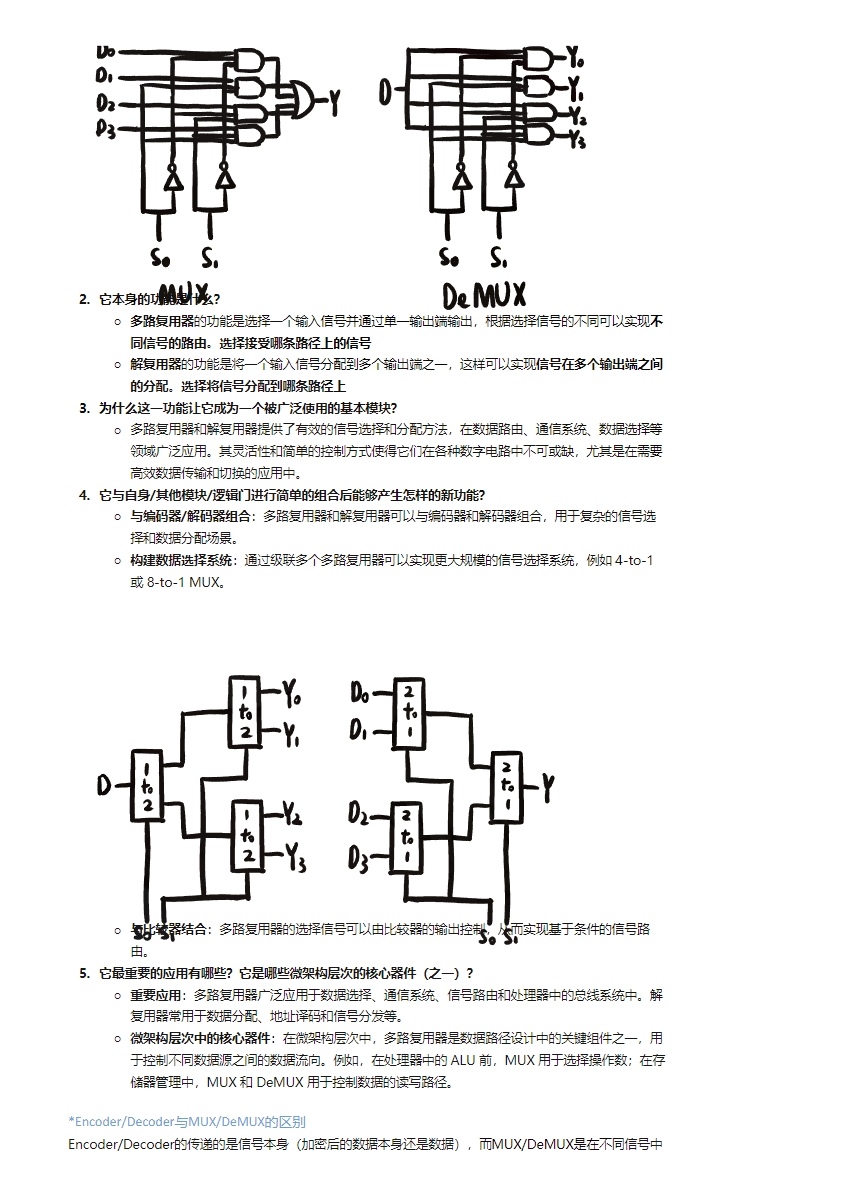
- 多路复用器(MUX)/解复用器(DeMUX):用于在多个信号之间进行选择和分配。
-
时序逻辑与记忆元件:
- 时序电路:与组合电路不同,时序电路中信息的输出不仅与当前输入有关,还与过去的状态相关。介绍了同步逻辑和异步逻辑的区别。
- 记忆元件:重点讲解了双稳态器件(如锁存器和触发器),它们是实现时序逻辑和存储数据的基本元件。
-
正负逻辑与混合逻辑:
- 解释了正负逻辑的概念,以及如何通过正负逻辑的转换来优化电路设计,利用逻辑门的等效性降低硬件成本。
This document provides a detailed overview of digital circuits and related concepts. The content covers various aspects, from number systems and logic gates to sequential circuits and combinational logic circuits. Below is a summary of the key points:
-
Number Systems and Conversion:
- It introduces the concept of place value systems, emphasizing the relationship between the position of digits and their corresponding weights in different bases. Common number systems such as decimal, binary, octal, and hexadecimal are discussed.
- The document explains how to convert between different bases, particularly the conversion methods between decimal and other number systems.
-
Logic Algebra and Boolean Algebra:
- It covers basic Boolean operations such as addition (OR), multiplication (AND), and negation (NOT), and introduces De Morgan’s Laws and the Consensus Theorem.
- Switching algebra is explained, along with its application in digital circuits. The document discusses logical expressions, truth tables, and simplification techniques such as Karnaugh maps (K-map) to simplify Boolean expressions.
-
Basic Circuit Modules:
- Adders: It explains the workings of half adders and full adders, their implementation, and their importance in digital systems.
- Comparators: Used to compare two binary numbers and output the result, commonly used in sorting and decision-making.
- Encoders/Decoders: Used to encode and decode information, helping with signal conversion and routing.
- Multiplexers (MUX) and Demultiplexers (DeMUX): Used to select and distribute signals among multiple lines.
-
Sequential Logic and Memory Elements:
- Sequential Circuits: Unlike combinational circuits, sequential circuits’ outputs depend not only on current inputs but also on past states. The document compares synchronous and asynchronous logic.
- Memory Elements: Focuses on bistable devices (such as latches and flip-flops), which are essential for implementing sequential logic and storing data.
-
Positive and Negative Logic and Mixed Logic:
- It explains the concept of positive and negative logic, and how to optimize circuit designs by using logical equivalences between them. The idea of using positive and negative logic transformations to reduce hardware costs is also explored.